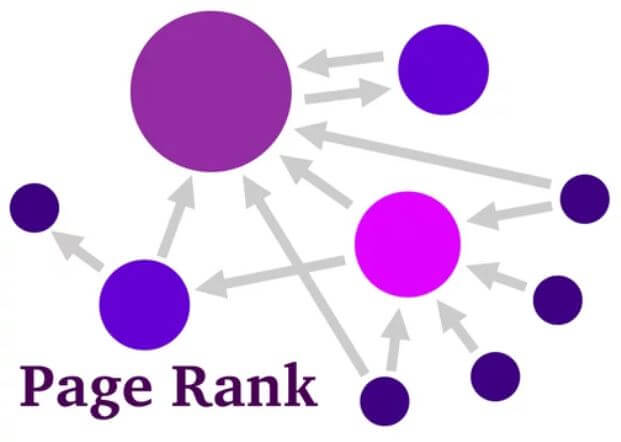
PageRank
Introduction
PageRank is an algorithm search engines use to rank web pages in their search engine results pages (SERPs). It was developed by Larry Page and Sergey Brin, the founders of Google, while they were still Ph.D. students at Stanford University. The PageRank algorithm assigns a score, from 0 to 10, to each web page based on the importance of the incoming links to that page. The higher the PageRank of a page, the higher its position in the search engine results in pages.
History of PageRank:
PageRank was first described in a paper by Larry Page and Sergey Brin in 1998, titled “The Anatomy of a Large-Scale Hypertextual Web Search Engine.” The original purpose of PageRank was to solve the problem of how to rank web pages based on the importance of their content without relying on the use of metadata and keyword density, which web admins could easily manipulate. The algorithm was named after Larry Page, and the term “PageRank” was trademarked by Stanford University.
Importance of PageRank:
PageRank is important because it is used by search engines, notably Google, to determine the relevance and authority of a webpage. The higher the PageRank score of a page, the more likely it is to rank higher in the search engine results in pages. PageRank is not the only factor that search engines use to rank web pages, but it is one of the most important. A high PageRank can increase the visibility and traffic of a website, while a low PageRank can have the opposite effect.
How PageRank Works
The concept of link analysis:
PageRank is a link analysis algorithm that measures the importance of web pages based on the quality and quantity of the links pointing to them. In other words, it assesses the popularity and relevance of a page based on the links from different carriers.
Importance of inbound links:
Inbound links, or backlinks, are links from other websites pointing to a specific web page. The more inbound links a page has, the more critical the PageRank algorithm considers it. However, not all inbound links are equal in value, and the PageRank algorithm considers the linking pages’ quality and relevance.
How the PageRank algorithm calculates the importance of a webpage:
The PageRank algorithm assigns a score, from 0 to 10, to each web page based on the importance of the incoming links to that page. The algorithm works by calculating the PageRank formula of each page based on the PageRank of the pages that link to it. The higher the PageRank of the linking page, the more weight it carries in calculating the page rank scores.
Let’s understand this with an example:
Suppose you have two web pages, A and B. Page A has two incoming links, one from Page C with a PageRank of 5 and one from Page D with a PageRank of 2. Page B has only one incoming connection from Page C with a PageRank of 5.
The PageRank of Page A would be higher than Page B’s, even though Page B has a link from a high PageRank page. Page A has two incoming links, one from a higher PageRank page, whereas Page B has only one.
Factors that affect PageRank:
Several factors can affect the PageRank of a web page, including the number and quality of inbound links, the relevance, and authority of the linking pages, the frequency and freshness of the content updates, and the use of keywords in the content.
The number and quality of inbound links are the most significant factors affecting PageRank. Pages with high-quality inbound links are considered more important than pages with fewer or lower-quality inbound links. The relevance and authority of the linking pages also play a role in determining the PageRank of a page. Pages linked to high-authority or relevant pages are considered more important than those related to low-authority or irrelevant pages.
The frequency and freshness of the content updates are also considered in the PageRank algorithm. Pages that are updated frequently and have fresh content are considered more important than pages that are rarely updated and have stale content. Lastly, using relevant keywords in the range can also affect the PageRank of a page. Pages that use relevant keywords in the field are considered more relevant to the search queries and are therefore given a higher PageRank.
Conclusion:
PageRank is a crucial algorithm search engines use to determine the relevance and importance of web pages. It assesses the quality and quantity of the links pointing to a page to determine its popularity and relevance. The PageRank algorithm assigns a score, from 0 to 10, to each web page based on the importance of the incoming links to that page. The higher the PageRank of a page, the more likely it is to rank higher in the search engine results in pages. Understanding the factors that affect PageRank can help web admins create better content and improve their SEO efforts.
Methods to Increase PageRank
Build high-quality inbound links:
The most effective way to increase PageRank is to build high-quality inbound links from authoritative and relevant websites. You can achieve this by creating valuable content other websites want to link to. You can also participate in link-building campaigns, guest posting on other websites, and collaborating with other businesses in your niche.
Improve your website’s internal linking:
Internal linking refers to linking between pages within your website. By improving your website’s internal linking, you can distribute PageRank more efficiently throughout your website, improving the PageRank of your pages.
Optimize your content:
Optimizing your content with relevant keywords and phrases can improve your page’s relevance to search queries and increase your PageRank. Use keywords in your page titles, headers, and content, but avoid overusing them, which can lead to keyword stuffing and hurt your PageRank.
Create fresh and engaging content:
Search engines love fresh and engaging content, which can help increase your PageRank. Regularly update your website with new and interesting content relevant to your target audience.
Use social media to promote your content:
Social media platforms can be an effective way to promote your content and build inbound links. Share your content on social media and engage with your audience to build a following and attract inbound links.
Use meta descriptions and tags:
Meta descriptions and tags are essential elements that summarize your web page’s content. Optimizing these elements with relevant keywords and phrases can improve your page’s relevance to search queries and increase your PageRank.
Improve your website’s loading speed:
Website loading speed is an essential factor that can affect your PageRank. A slow-loading website can frustrate users and lead to a higher bounce rate, negatively impacting your PageRank. To improve your website’s loading speed, optimize your images, use caching, and reduce the number of HTTP requests.
Conclusion:
Increasing your PageRank is essential to improving your website’s search engine visibility and driving organic traffic. By building high-quality inbound links, optimizing your content, creating fresh and engaging content, using social media to promote your content, improving your website’s internal linking, using meta descriptions and tags, and improving your website’s loading speed, you can increase your PageRank and enhance your website’s search engine visibility. Remember, improving your PageRank is an ongoing process that requires consistent effort and optimization.
Common PageRank Misconceptions
PageRank is the only factor that affects search engine rankings:
While PageRank is an essential factor that affects search engine rankings, it is not the only factor. Search engines use a complex algorithm that considers many factors, including the relevance and quality of the content, the user experience, the website’s loading speed, and the presence of relevant keywords and phrases.
The higher the PageRank, the higher the search engine ranking:
While a higher PageRank can improve your website’s search engine ranking, it is not the only factor. Other factors, such as the relevance and quality of the content, the user experience, and the website’s loading speed, can also affect your search engine ranking.
PageRank can be manipulated by buying links:
While buying links may seem like an easy way to increase your PageRank, it violates search engine guidelines and can result in penalties or even a complete ban from search engine results pages.
PageRank is the same as website traffic:
While PageRank can improve your website’s search engine visibility and drive organic traffic, it is not the same as website traffic. Website traffic refers to the number of visitors your website receives, while PageRank measures your website’s importance in search engines’ eyes.
A low PageRank means your website is not successful:
A low PageRank does not necessarily mean that your website is not successful. There are many successful websites with a low PageRank and many unsuccessful websites with a high PageRank. Ultimately, your website’s success depends on various factors, including the relevance and quality of the content, the user experience, and the website’s loading speed.
Conclusion:
PageRank is an important factor that affects search engine rankings, but it is not the only factor. Common misconceptions, such as thinking that PageRank is the same as website traffic or that it can be easily manipulated by buying links, can lead to poor decision-making and hurt your website’s search engine visibility. Understanding the role of PageRank in search engine optimization and the factors that affect search engine rankings can help you make informed decisions and improve your website’s search engine visibility.
PageRank and SEOs
PageRank is an important factor that affects search engine optimization (SEO). Understanding how PageRank works and how it can impact your website’s search engine visibility is essential to improving your website’s SEO.
Importance of PageRank in SEO:
PageRank is an important factor that search engines use to determine the importance and relevance of a website. A higher PageRank can improve your website’s search engine visibility and drive organic traffic, improving your website’s SEO.
Factors that impact PageRank:
Several factors impact PageRank, including the number and quality of inbound links, the relevance and quality of the content, and the user experience. Understanding and optimizing these factors can help improve your website’s PageRank and SEO.
The role of inbound links:
Inbound links are links from other websites that point to your website. The number and quality of inbound links are important factors that affect your PageRank and SEO. Building high-quality inbound links from authoritative and relevant websites can improve your website’s PageRank and SEO.
The importance of content:
The relevance and quality of your website’s content is an essential factor that affects your PageRank and SEO. Creating fresh, engaging, and relevant content can improve your website’s search engine visibility and attract high-quality inbound links.
User experience:
The user experience is an essential factor that affects your website’s PageRank and SEO. A positive user experience, such as a fast-loading website, easy navigation, and mobile optimization, can improve your website’s search engine visibility and attract high-quality inbound links.
PageRank and keyword optimization:
Optimizing your website’s content with relevant keywords and phrases is an essential factor that affects your PageRank and SEO. Using keywords in your page titles, headers, and content can improve your page’s relevance to search queries and increase your PageRank.
PageRank and website structure:
The structure of your website can impact your PageRank and SEO. A well-structured website with a clear hierarchy and internal linking can distribute PageRank more efficiently and improve your website’s search engine visibility.
Conclusion:
PageRank is an important factor that affects SEO. Understanding how PageRank works and the factors that impact it can help you improve your website’s search engine visibility and drive organic traffic. You can improve your website’s PageRank and SEO by building high-quality inbound links, creating fresh and engaging content, optimizing for relevant keywords, improving the user experience, and optimizing your website’s structure.
Final Conclusion:
PageRank is a complex algorithm used by search engines to measure the importance and relevance of a website. It is a critical factor that affects search engine rankings and can significantly impact your website’s visibility and organic traffic.
To improve your website’s PageRank, you need to focus on several factors, including the quality and relevance of your content, building high-quality inbound links, optimizing for relevant keywords, improving the user experience, and optimizing your website’s structure. These factors strengthen your website’s search engine visibility and drive organic traffic.
It is essential to understand that PageRank is not the only factor that affects search engine rankings. Search engines use a complex algorithm that considers many other factors, including the relevance and quality of the content, the user experience, and the website’s loading speed. Focusing on these factors can improve your website’s search engine visibility and drive organic traffic.
In addition, there are common misconceptions about PageRank, such as thinking it is the same as website traffic or can be easily manipulated by buying links. Understanding the role of PageRank in search engine optimization and the factors that affect search engine rankings can help you make informed decisions and improve your website’s search engine visibility.
In summary, PageRank is an essential factor that affects search engine optimization, but it is not the only factor. By creating high-quality content, building high-quality inbound links, optimizing for relevant keywords, improving the user experience, and optimizing your website’s structure, you can improve your website’s PageRank and SEO and drive organic traffic.
F.A.Q
What is PageRank used for?
Search engines use PageRank to measure the importance and relevance of a website’s pages. It is one of the many factors search engines use to determine the order in which web pages are presented in search results for a given query. PageRank is used to help search engines provide more relevant and valuable search results to users by ranking web pages based on their perceived authority and relevance. This can increase visibility and organic traffic for websites with higher PageRank. Additionally, PageRank can be used by website owners and marketers to help improve their website’s search engine optimization (SEO) by optimizing their content, building high-quality inbound links, and improving the user experience.
Is PageRank still used today?
PageRank is still used today, but its role has evolved. Initially developed by Google in the late 1990s, PageRank was a critical factor in Google’s search algorithm and was used to determine the relevance and authority of web pages. However, as search engine algorithms have become more complex and sophisticated, PageRank’s importance has diminished somewhat. Today, PageRank is just one of many factors that search engines use to determine the relevance and authority of web pages. Other factors include the quality and relevance of the content, the user experience, the website’s loading speed, and the site’s mobile-friendliness.
PageRank is still essential for website owners and marketers looking to improve their website’s search engine optimization (SEO). While PageRank is no longer publicly visible, various tools and metrics can help website owners assess the quality and authority of their website’s pages. These metrics include domain authority, page authority, citation flow, and trust flow. By improving these metrics and building high-quality inbound links, website owners can improve their website’s visibility in search engine results pages (SERPs) and drive more organic traffic.
How is PageRank calculated?
PageRank is calculated using a complex algorithm that considers various factors, including the quality and relevance of a web page’s content, the number and quality of inbound links pointing to the page, and the website’s overall structure. While the exact algorithm used by search engines like Google is proprietary and not publicly available, the following is a general overview of how PageRank is calculated:
- First, the algorithm assigns an initial value of 1 to each page in the web graph.
- The algorithm then calculates a PageRank for each page based on the number and quality of inbound links pointing to that page. Pages receiving more inbound links from high-quality, authoritative sources will generally have a higher PageRank than pages with fewer inbound links or low-quality references.
- The algorithm also considers the importance and relevance of the pages linking to the target page. Links from pages that are themselves highly relevant and authoritative will generally carry more weight than links from less important or less relevant pages.
- The algorithm continues iterating through the web graph until the PageRank for all pages has converged to a stable value. At this point, each page is assigned a final PageRank, which search engines use to rank pages in search results.
It’s worth noting that while PageRank is an essential factor in search engine rankings, it is just one of many factors that search engines use to determine the relevance and authority of web pages. Other factors, such as the quality and relevance of a page’s content, the user experience, and the website’s loading speed, also play a role in determining search engine rankings.
Why did Google stop using PageRank?
Google did not necessarily “stop” using PageRank; instead, they stopped publicly displaying it for individual pages. In 2016, Google officially removed PageRank from its toolbar and stopped updating the public PageRank.
There are several reasons why Google stopped displaying PageRank, including:
- Spam: Over time, many website owners and marketers became obsessed with increasing their PageRank, often resorting to unethical tactics like buying links or engaging in link exchanges. This led to a proliferation of spammy, low-quality websites with high PageRank, which degraded the overall quality of Google’s search results.
- Complexity: As Google’s search algorithm became more sophisticated, PageRank became just one of many factors the algorithm considered. Google realized that it was becoming increasingly difficult to accurately represent the importance and relevance of individual pages using a single, static score.
- User Experience: Google ultimately decided that displaying the PageRank was irrelevant to most users. Instead, Google focused on other metrics and features that could provide more valuable information to users, such as rich snippets, featured snippets, and related searches.
While Google may have stopped displaying PageRank publicly, it is still believed to be an important factor in Google’s search algorithm. However, other factors, such as the quality and relevance of content, user experience, and website structure, are also essential considerations for search engine rankings.