Lifetime value (LTV)
Introduction
Many metrics can be used to measure a business’s success, such as revenue, profit, and market share. However, one of the most critical metrics for a company to track is the lifetime value (LTV). LTV is a measure of the total revenue a customer will generate for a business throughout their lifetime as a customer. In other words, it is the amount of money a customer is expected to spend on a company’s products or services throughout their relationship.
Importance of Lifetime Value
LTV is important for several reasons. First, it helps businesses understand the long-term value of their customers. By knowing the LTV of a customer, a company can make better decisions about how much to spend on customer acquisition and retention. Second, LTV can help businesses identify which customers are most valuable. By identifying high LTV customers, a company can focus its marketing and retention efforts on those customers. Third, LTV can help a company understand how much it can afford to spend to acquire new customers. By knowing the LTV of a customer, a company can calculate the maximum amount it can pay to receive a new customer while still generating a positive return on investment.
Calculating Lifetime Value:
Calculating the LTV of a customer can be a complex process, but it is an essential tool for any business looking to maximize its revenue and profitability. The basic formula for calculating LTV is:
LTV = Average Order Value x Number of Purchases per Year x Average Customer Lifespan
Let’s take a closer look at each of these variables:
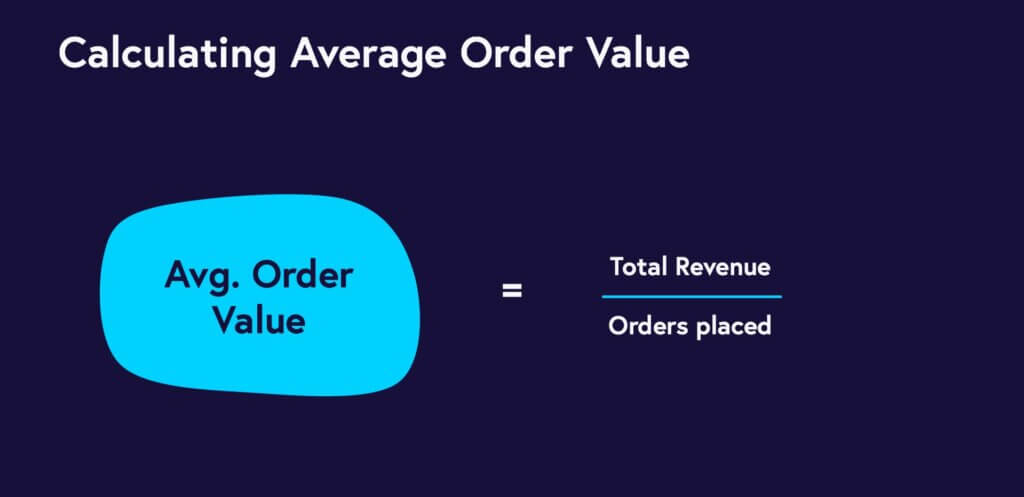
Average Order Value:
The average order value is the average amount of money a customer spends each time they make a purchase. This can be calculated by dividing the total revenue generated by the number of orders. For example, if a business generates $100,000 in revenue from 1,000 orders, the average order value would be $100.
Number of Purchases per Year:
The number of purchases per year is the average number of times a customer purchases. This can be calculated by dividing the total number of orders by the number of customers. For example, if a business had 1,000 orders from 100 customers in a year, the number of yearly purchases would be 10.
Average Customer Lifespan:
The average customer lifespan is when a customer remains loyal to a business. This can be calculated by dividing the total number of years a customer remains a customer by the total number of customers. For example, if a business has 1,000 customers and the average customer remains a customer for five years, the average customer lifespan would be five years.
Examples:
Let’s see an example of how the LTV formula works in practice. Assume a business has an average order value of $100, customers make an average of 10 purchases per year, and the average customer lifespan is five years. The LTV of a customer for this business would be:
LTV = $100 x 10 x 5 = $5,000
The average customer is expected to spend $5,000 on the business’s products or services over five years.
It’s important to note that this is a simplified example, and many variables can affect LTV, such as customer acquisition costs and churn rate. However, the basic formula can be a valuable tool for businesses to understand the potential value of their customers and make better decisions about allocating resources to customer acquisition and retention.
Calculating LTV is essential for any business looking to maximize revenue and profitability. By understanding the value of their customers over time, companies can make informed decisions about how much to invest in customer acquisition and retention and identify which customers are most valuable to their bottom line.
Strategies to Increase Lifetime Value
Once a business has calculated the LTV of its customers, the next step is to find ways to increase that value. Here are some strategies companies can use to increase LTV:
Customer Retention:
One of the most effective ways to increase LTV is to focus on customer retention. Retaining existing customers is much less expensive than acquiring new ones and can lead to higher revenue over time. Here are some strategies businesses can use to improve customer retention:
- Personalization: Personalizing the customer experience can help businesses build stronger customer relationships. This can be achieved through targeted marketing campaigns, personalized product recommendations, and customized customer service.
- Loyalty Programs: Implementing a loyalty program can incentivize customers to continue making purchases with a business. Rewards can include discounts, free products or services, and exclusive offers.
- Exceptional Customer Service: Providing excellent customer service can go a long way in retaining customers. This includes responding promptly to inquiries and complaints, offering refunds or exchanges when necessary, and going above and beyond to solve customer problems.
Upselling and Cross-Selling:
Another way to increase LTV is to encourage customers to make additional purchases. Upselling involves convincing customers to purchase a higher-end product or service, while cross-selling involves offering complementary products or services. Here are some strategies businesses can use to increase upselling and cross-selling:
- Product Bundles: Bundling products or services together can make it easier for customers to purchase additional items. For example, a business selling a computer could bundle it with a printer and other accessories.
- Personalized Recommendations: Providing customized product recommendations based on a customer’s purchase history can increase the likelihood of them making additional purchases.
Product and Service Improvements:
Improving the quality of products or services can help businesses retain existing customers and attract new ones. Here are some strategies companies can use to improve their products or services:
- Product Development: Investing in product development can lead to new and improved products that better meet customers’ needs. This can involve conducting market research to identify customer needs and preferences.
- Service Improvements: Improving customer service can increase customer satisfaction and retention. This can involve training staff to provide better service, improving response times to inquiries and complaints, and offering more convenient and flexible service options.
Referral Programs:
Referral programs can incentivize customers to refer their friends and family to a business. This can help companies to acquire new customers at a lower cost than traditional marketing methods. Here are some strategies companies can use to implement referral programs:
- Incentives: Offering incentives such as discounts or free products or services can encourage customers to refer their friends and family.
- Easy Referral Process: Making the referral process easy and convenient can increase the likelihood of customers referring others. This can involve providing referral links or codes that can be easily shared via social media or email.
Increasing LTV is essential for businesses looking to maximize revenue and profitability. By focusing on customer retention, upselling and cross-selling, product and service improvements, and referral programs, companies can increase the value of their customers over time and improve their bottom line.
Challenges in Maximizing Lifetime Value:
While increasing LTV can lead to higher revenue and profitability, there are several challenges that businesses may face. Here are some of the key challenges companies may encounter when trying to maximize LTV:
Cost of Acquisition:
One of the biggest challenges in maximizing LTV is the cost of acquiring new customers. Businesses must invest in marketing and advertising to attract new customers, which can be expensive. If the acquisition price is too high, it generates a positive return on investment.
Churn Rate:
Another challenge businesses may face a high churn rate. The churn rate is when customers stop doing business with a company. High churn rates can reduce LTV, as businesses need to acquire new customers to replace those who have left continually. Companies must focus on improving customer satisfaction and retention to reduce churn rates.
Competition:
Competition can also be a challenge in maximizing LTV. If many businesses offer similar products or services, customers may be more likely to switch to a competitor if they offer better prices or customer experience. To compete effectively, businesses must differentiate themselves and provide a unique value proposition.
Changing Customer Needs:
Customer needs and preferences can change over time, which can impact LTV. If a business cannot adapt to changing customer needs, it may lose customers to competitors. Companies must conduct regular market research and invest in product and service development to stay ahead of changing customer needs.
To overcome these challenges and maximize LTV, businesses must take a proactive approach. Here are some strategies companies can use to overcome these challenges:
- Customer Segmentation: By segmenting customers based on their needs and preferences, businesses can provide more personalized experiences that are more likely to lead to higher LTV.
- Customer Feedback: Regularly soliciting customer feedback can help businesses identify areas for improvement and make changes to meet customer needs better.
- Continuous Improvement: By continually improving products, services, and customer experiences, businesses can stay ahead of competitors and retain customers for extended periods.
While maximizing LTV can lead to higher revenue and profitability, there are several challenges that businesses may face. By addressing these challenges through customer segmentation, feedback, and continuous improvement, companies can increase LTV and stay ahead of competitors.
Conclusion:
Lifetime value (LTV) is a crucial metric for businesses looking to maximize their revenue and profitability. LTV measures the total income a customer is expected to generate for a business throughout their entire relationship with the company. By understanding LTV, businesses can decide how much to invest in customer acquisition and retention and identify which customers are most valuable to their bottom line.
To calculate LTV, businesses must consider average orders, yearly purchases, and average customer lifespan. Once LTV is calculated, companies can use various strategies to increase it, including customer retention, upselling and cross-selling, product and service improvements, and referral programs.
However, there are several challenges businesses may face in maximizing LTV, including the cost of acquisition, churn rate, competition, and changing customer needs. Companies must take a proactive approach to overcome these challenges, including customer segmentation, customer feedback, and continuous improvement.
LTV is a powerful metric that can help businesses make informed decisions about customer acquisition and retention and maximize revenue and profitability. By understanding the importance of LTV and proactively increasing it, companies can improve their bottom line and stay ahead of the competition.
F.A.Q
What is the importance of customer lifetime value?
Customer lifetime value (LTV) is an essential metric for businesses because it helps them understand the long-term value of their customers. LTV measures the total revenue a customer is expected to generate for a business over their entire relationship with the company.
Understanding LTV is essential for several reasons. First, it can help businesses decide how much to spend on customer acquisition and retention. By knowing the LTV of a customer, a company can calculate the maximum amount it can pay to acquire a new customer while still generating a positive return on investment.
Second, LTV can help businesses identify which customers are most valuable. By identifying high LTV customers, a company can focus its marketing and retention efforts on those customers, leading to higher revenue and profitability.
Third, LTV can help a business understand how much it can afford to spend on improving the customer experience. By knowing the LTV of a customer, a company can invest in initiatives that will enhance customer satisfaction and retention, leading to higher LTV and profitability over time.
Overall l, understanding lifetime value is critical for any business looking to maximize revenue and profitability. By focusing on increasing LTV through strategies such as customer retention, upselling and cross-selling, and product and service improvements, businesses can improve their bottom line and stay ahead of the competition.
What is the difference between CLV and LTV?
Customer Lifetime Value (CLV) and Lifetime Value (LTV) are related concepts that are sometimes used interchangeably but are not precisely the same.
CLV refers to the total value of a customer over the entire duration of their relationship with a business. This includes both past and future transactions. CLV considers the customer’s purchase history, purchase frequency, and each asset’s average value.
On the other hand, LTV measures the total revenue a customer is expected to generate for a business throughout their entire relationship with the company. LTV is a forward-looking metric that predicts the future revenue a customer will develop based on historical data.
While CLV and LTV are similar, the two have a few key differences. The main difference is that CLV includes past and future transactions, while LTV is focused on predicting future revenue based on past behavior. CLV is also more comprehensive, considering all trades, while LTV is a simplified calculation that expects future revenue.
In summary, CLV and LTV are related metrics that measure the value of a customer, but they have different focuses and calculations. CLV is a more comprehensive metric that includes past and future transactions, while LTV is a simplified calculation that predicts future revenue based on past behavior.